A cryptocurrency is a digital currency that only exists in a network of computers called a ‘blockchain’ on the internet. They are virtual currencies that are decentralised and exist outside of traditional banking but can still be traded like any other currency.
Bitcoin is the original and best-known cryptocurrency but there are now 1000s of cryptocurrencies based on the same technology.
How do cryptocurrencies work?
Cryptocurrencies are a kind of digital cash with no central authority, meaning no one person or institution (like a central bank) controls it. The idea is similar to a Peer-to-Peer network for file sharing i.e. everybody on the network shares the files, they are not stored on just one computer.
Having no central authority removes the need for any one entity to be trusted with control of the accounts, balances and transactions. In other words, it improves transparency and reduces the risk of fraudulent accounting or errors like ‘double spending’ within the system.
Newly created cryptocurrencies like a bitcoin are entered into a database known as the blockchain. The currencies are created when computers crunch a complex set of algorithms in a process called mining. These algorithms use cryptography to secure transactions and regulate the creation of additional units of the cryptocurrency.
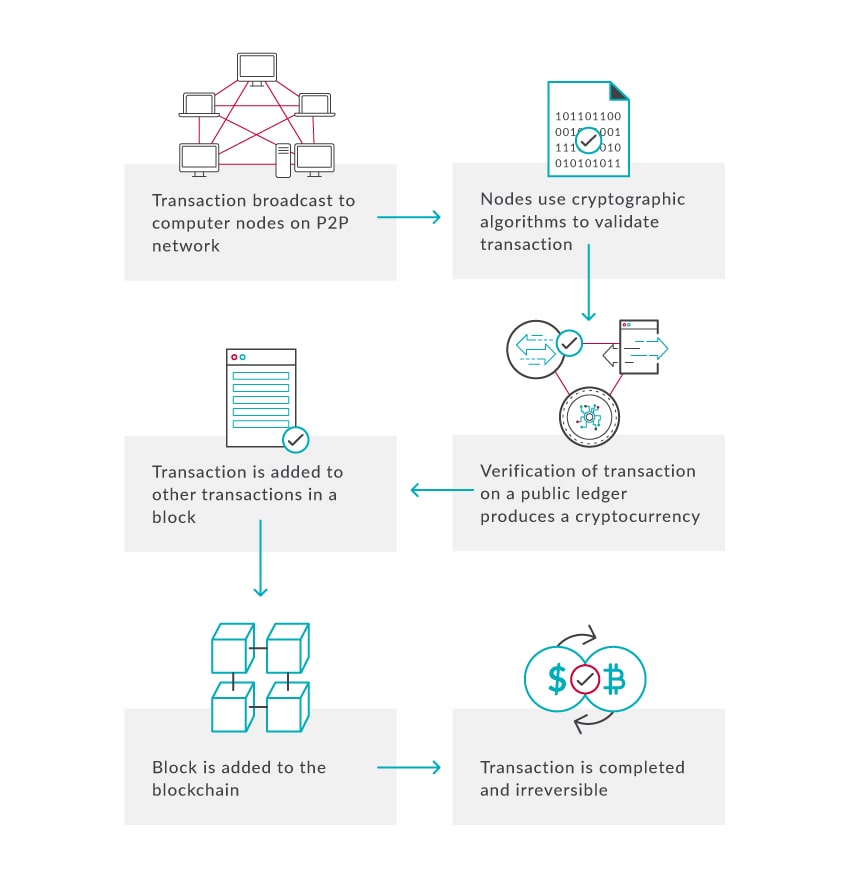
Within the network, every peer has a record of the complete history of all transactions and thereby every account balance. The cryptocurrency exists as a way to show a financial transaction. See the lifecycle of a transaction below.
The transaction lifecycle
What is Blockchain technology?
All cryptocurrency transactions are stored in a digital, decentralised public ledger called a Blockchain. Each new transaction represents a new ‘block’ in the ‘chain’ of all transactions. A blockchain makes use of distributed ledger technology (DLT) to account for digital currency transactions. Cryptocurrency users can track every transaction ever made via the blockchain, however, the name of the user making the transactions is anonymous. A copy of the blockchain is downloaded on every node of the network, making the need for a central record redundant.
What is Cryptocurrency Mining?
Cryptocurrency (or Crypto coin or Altcoin) mining is the process of verifying cryptocurrency transactions. Digital Miners do not use a pickaxe but instead, powerful computer algorithms to crunch complex cryptographic puzzles. Miners are rewarded with some new coins for every transaction that is verified and added to the blockchain. Anybody can be a miner with the right hardware but the mining of Bitcoin, Ethereum and other popular cryptocurrencies are now dominated by large-scale operations, located in areas with low electricity costs.
What is Cryptography?
Cryptography uses mathematical codes to keep information secret. A user can only read the encrypted message if they know the key that will translate it to normal language. In the age of computers, the cryptography is too complex for a human brain to decipher so computer algorithms both encrypt and decrypt. One of the most famous examples of the use of cryptography is the Enigma machine used by Nazi Germany in World War II, which was eventually decoded by British cryptologists at Bletchley Park.
How to use cryptocurrencies
Cryptocurrencies were designed to provide an alternative way to make payments and transactions online but they are yet to be widely adopted. It is the belief that, one day, cryptocurrencies will (or will not) be widely adopted that has caused all the speculation in the last few years. In essence, investors are betting that cryptocurrencies will be used as money.
As a reminder, money is supposed to serve three purposes:
- A medium of exchange (can be used to buy and sell things)
- A unit of account (divisible into units that can represent the true value of different things)
- Store of value (keeps its value over time)
There is a lot of debate about whether cryptocurrencies are able to serve these qualities.
For the time being at least, the main problem with using cryptocurrencies as money is the volatility of the price. Because they are so volatile, not many merchants accept cryptocurrencies as a method of payment, the price of a good or service would have to change day to day to keep up and the price changes too much to rely on it to hold its value. All these things could start to change if the price stabilises.
The debate over ‘scarcity’
In the case of Bitcoin, it is widely believed by mainstream economists that an economy could not function with only 21 million units that will ever be issued. Under the current monetary system, banks can create an unlimited new supply of money through banks loans. The value of the ‘fiat’ currencies under the current monetary system (like the US dollar) is eroded over time by inflation.
Bitcoin was supposedly modelled after precious metals like gold (i.e. mining) on the basis that scarcity helps maintain value. There is only so much gold that can be mined out of the ground and one day there will be none left or it will be too expensive to make it worthwhile mining. The Proponents of Bitcoin argue that the coins are divisible to smaller units, which will gain in value once the total supply of bitcoins has been mined.
Most popular cryptocurrencies
Bitcoin (BTC)
Bitcoin is the best known, most expensive and the original cryptocurrency. Satoshi Nakamoto, whose real identity has never been completely proven, created Bitcoin in 2009. Bitcoin is so prominent that every other crypto coin is called an altcoin, i.e. an alternative to Bitcoin. The big price tag for each Bitcoin has seen investors turn to altcoins. The trick for investors is to find altcoins that in the future may co-exist with or eventually replace Bitcoin. Most altcoins purport to find solutions to some of the imperfections of Bitcoin- especially its limited scalability. So far, the market capitalisation of Bitcoin remains far and above the nearest alternatives.
Ethereum (ETH)
Ethereum is a distributed public blockchain network created in 2015. The main difference between Ethereum and Bitcoin is the function of the network. Instead of being used to track ownership of cryptocurrencies, Ethereum is used to run programming code for decentralised applications. The Ethereum network has its own tokens, which are called Ether. Ether is what is traded but it is frequently mistakenly referred to as Ethereum. The central premise is that anyone who wishes to use blockchain technology can piggyback on Ethereum without building a completely new application. Many new altcoins launched through the Ethereum network, with the larger ones like EOS, Zilliqa and RChain eventually launching independent blockchains.
Ripple (XRP)
Ripple is a means to transfer money but works differently to the Bitcoin network. It does not use blockchain technology and is not restricted to the transfer of its own coins. Ripple enables the transfer of any kind of currency including cryptos, fiat currencies, gold and even air miles. Banks have had a strong interest in Ripple because of the speed of transactions (10,000x faster than Bitcoin). The Ripple protocol has its own tokens, which can be traded but 100,000 of the tokens were issued like company shares, rather than being mined.
EOS (EOS)
EOS is the native cryptocurrency of the EOS.IO blockchain protocol launched in 2017. The purpose is to operate as a smart contract platform and decentralised operating system to host decentralised applications and offer decentralised storage. EOS.IO aims to solve the scalability problems of older blockchains like Bitcoin as well as eliminate all fees for users in traditional areas of finance. The EOS token which is traded is used to gain bandwidth and storage on the blockchain for the applications being created/used by the account holder.
Bitcoin Cash (BCH)
Bitcoin cash is the best known ‘hard fork’ of Bitcoin Classic (the original Bitcoin). A hard fork is creating a brand new currency based on the existing Bitcoin technology. The main reason to create the fork was to add scalability. The biggest change was increasing the size of the blocks to allow the processing of more transactions per second (i.e. it is faster).
How to trade Bitcoins
Whatever the ultimate fate of cryptocurrencies, the markets are very active and provide ample trading opportunities
Read the LCG guide on How to trade Cryptocurrencies
 Change Language ▼
Change Language ▼

